Con este post pretendo intentar detectar problemas de una manera básica entre nodos de nuestra Lan que tengan por medio switches o routers, problemas que se salgan de lo básico sin llegar a un nivel muy alto mediante comandos estandart de Microsoft.
En función a la prueba obtendremos unos tiempos/latencias diferentes, ya sea por la electrónica, por el medio de conexiòn que tengamos, etc ... .
[1] Ping básico
Ping en nuestra propia Red. Si este comando no responde, normalmente prodía deberse a que está apagado el host contra el que estamos haciendo ping o tiene algún programa que evite contestar (como por ejermplo un firewall, ACL del switcth...).
Ping a través de una línea externa RDSI
Ping a través de una F.O.
Lo mas significativo de estás 3 imágenes son los tiempos en función a la calidad del servicio de las líneas.
Otro caso de porque no podría responder un ping podría ser debido a que tuviesemos el gateway mal configurado o que algún elemento entre los 2 nodos no sepa devolver el paquete.
[2] Ping –a. Con resolución de nombres DNS
Es importante si accedemos a los nodos por nombre en lugar de por IP.
Puede resolver el nombre aunque tengamos la máquina apagada.
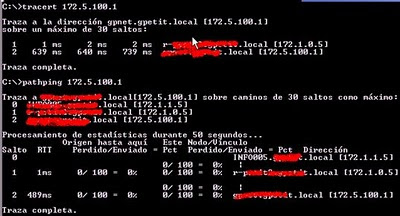
[3] Tracert
Es útil si hay routers por medio.
En nuestra LAN en la que hay switches no aporta mucha información.
Si pasamos por router nos informa por los que hemos pasado para llegar al destino y sus tiempos:
[4] Verificar la MTU
A veces necesitamos verificar la MTU cuando pasamos entre routers, una manera de hacerlo sería modificando el tamaño del paquete.
El tamaño estandar de un paquete ping icmp es de 32 bytes. Si tenemos problemas podemos ir disminuyendo/aumentando hasta encontrar el tamaño con el que pase sin errores.
ping -l tamañoMTP IPDestino
ping -l 1000 172.5.100.1
ping -l 1000 172.5.100.1
Lo mejor sería hacerlo sin fragmentar -f
Muchos routers tienen un tamaño de 1500 en su MTU. Si sumamos cierta seguridad a los paquetes eso incrementa su tamaña haciendo que no se corresponda con el definido en los enrutadores ocasionado problemas.
[5] Pathping
Un nuevo comando que apareció a partir de las Windows 2000, es una mezcla de un ping parametrizado y un tracert.
MÁS COSAS A CONSIDERAR:
Entrar en los Switches a través de Telnet/SSH/http/https ...
Sería de gran ayuda verificar los puertos de los routers si establencen la conexión correctamenet:
FD/HD/AUTO
10/100/1000
Bloqueado por alguna regla (ACL)
... que no pertenezca a otra Vlan
Bloqueado por alguna regla (ACL)
Con este pantallazo ves si se han incrementado las coincidencias en reglas aplicadas
... que no pertenezca a otra Vlan
Que no haya paquetes perdidos, con errores, bloqueados o retrasmisiones
También se puede hacer através del entorno gráfico, pero misteriosamente no siempre se corresponde.
No puede haber colisiones en conexiones FD.
No pueden haber 2 caminos ACTIVOS para llegar a un host (Peligrosisimo!!)
Existen herramientas que nos pueden ser tremendamente útilies para ver los paquetes que van por nuestra red y/o que máquinas lo están generando como Wireshark o Sysinternals.
También nos puede ser útil el post: http://gonsystem.blogspot.com/2010/10/troubleshooting-problemas-red.html